The objective of this tutorial will be to introduce you to the concept of the shape operator and its importance in 3D modelling - such as that used to model the cortical surface of the brain.
Let's begin at the beginning, with a simple plane curve.
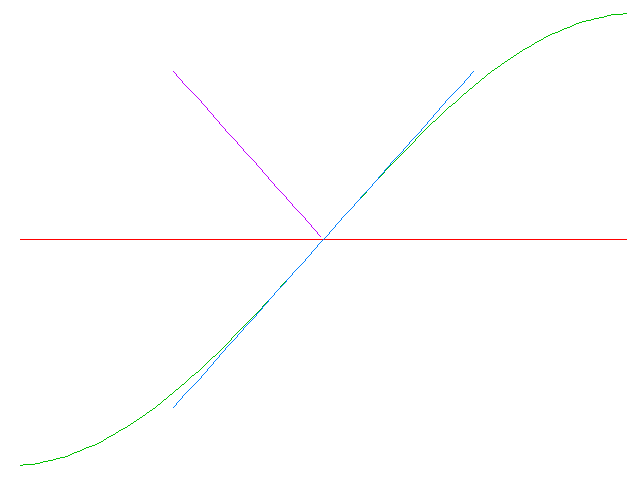
If we take a line and deform it slightly, we create a plane curve (meaning a 1-dimensional curve). Each point on this plane curve, furthermore, has a unique tangent and normal that can be defined in terms of the derivative of the curve at that point.
The tangent line is defined as a line that intersects this curve at only one point, and has a slope that is equal to the derivative of the curve at that point.
The normal line, on the other hand, is defined as a line that is perpendicular to the tangent line at that point, and has a slope that is the negative inverse of the tangent. In other words, if the slope of the tangent line is 2, the slope of the normal line is -1/2.